Research for Development of Semiconductor Cleaning Agents and Eco-cleaning Processes as Support for Future IoT Society
Precision Industry / Electronics
Semiconductors are commonly used and make our lives safe, secure, and convenient, while their demand is increasing with development of an IoT society. Hundreds of processes are involved in semiconductor manufacturing, with large amounts of CO2 emitted by long periods of ultrapure water and chemical use, especially during the cleaning process.
Kao is working on development of cleaning agents for better cleaning and significant reductions in CO2 emissions for the semiconductor industry, which is attracting worldwide attention. A primary factor in the long-term cleaning is that silica particles used for polishing remain adhered to the substrate when brought into the cleaning process.
Residual silica greatly affects the yield of semiconductor substrates, with approximately 7 trillion silica particles sized 100 nanometers or smaller attached to a substrate with a diameter of 30 cm, and such nano-sized fine particles cannot be removed by water rinsing alone. Therefore, long-term cleaning with a large amount of ultrapure water or chemicals is necessary to reduce their number to zero.
Kao considered that the rinsing time could be effectively shortened by significantly reducing the amount of silica brought into the cleaning process. We have developed a pre-cleaning agent that has both a cleaning effect to remove fine silica particles and a hydrophilic effect that prevents contamination of the substrate surface. A pre-cleaning process used immediately after polishing was introduced to the polishing machine, and successful removal of a significant amount of silica adhesion by simply rinsing with the pre-cleaning agent for only a few tens of seconds was noted. Currently, we are proceeding with verification to reduce the cleaning process and amount of CO2 emissions.
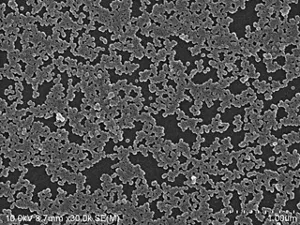
Non-treatment

Treatment by Kao Agent
Related Information
- Home
- Innovation
- Research & Development
- Product Development Research
- Industrial Chemicals
- Research for Development of Semiconductor Cleaning Agents and Eco-cleaning Processes as Support for Future IoT Society
- Home
- Innovation
- Research & Development
- Product Development Research
- Industrial Chemicals
- Research for Development of Semiconductor Cleaning Agents and Eco-cleaning Processes as Support for Future IoT Society
