Kao Accelerating Efforts to Reach Carbon Zero by 2040 and Carbon Negative by 2050
100% of Electricity Purchased in Japan Was from Renewable Energy Sources; Medium-term Target for Reducing Scope 1+2 CO2 Emissions Achieved Two Years Ahead of Time
By implementing Innovation in Reduction and Innovation in Recycling with regard to CO2, Kao Corporation is aiming to achieve carbon zero by 2040, and carbon negative by 2050 in its business activities. In April 2019, Kao established its ESG strategy, the Kirei Lifestyle Plan, which outlines 19 leadership actions, one of which is decarbonization. In 2023, 100% of electricity purchased by Kao in Japan came from renewable energy sources, and the company reached the target of reducing Scope 1+2*1 CO2 emissions (absolute value) by 28% by 2025 two years ahead of time. The following describes this and other progress made in 2023.
-
* 1 The volume of greenhouse gases emitted directly by business enterprises and other organizations.
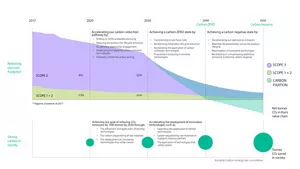
Kao’s decarbonization goals
Innovation in CO2 Reduction/Targets to Achieve Carbon Zero by 2040 and the 2023 Results
Continuing measures previously implemented, in 2023 Kao actively adopted energy-efficient production facilities and decarbonization technology, and further drove the transition to renewable energy. In July, the company announced that it had built its first biomass thermal power generation plant at its chemical plant in Spain, reducing the plant’s CO2 emissions by 95%. Use of the internal carbon price system of $168/ton-CO2 also continues in our operations in Japan and overseas. In 2023, introduction of a water heat pump system at the Wakayama Plant in Japan (scheduled to begin operating in April 2024) and a photovoltaic power generating facility at the Kao Industrial Thailand plant (scheduled to begin operating in January 2025) were approved. And in April, in a first for Kao, the company adopted virtual Power Purchase Agreement (VPPA), a type of corporate Power Purchase Agreement*2 . By continuing to adopt renewable energy, Kao was able to purchase 100% of its electricity in Japan from renewable energy sources by the end of 2023. Thanks to these activities, the company succeeded in reaching its medium-term target of reducing Scope 1+2 CO2 emissions (absolute amount) by 28% by 2025, two years earlier than planned.
-
* 2 Scheme whereby users enter into long-term agreements directly with energy retailers to buy renewable energy.


Water heat pumps at the Toyohashi Plant (left, completed in May 2023) and photovoltaic power generation facility at the Kashima Plant (right, completed in January 2024), both approved in 2022 through the internal carbon price system
-
By 2030, Kao will have reduced Scope 1+2 CO2 emissions (absolute value) by 55% (taking 2017 as the base year)*3
*28% reduction by 2025 (taking 2017 as the base year)
2023 results: 35% (2022: 26%)
-
* 3 Certified by the global Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) as a 1.5°C target.
-
By 2030, 100% of the electricity used will be sourced from renewable energy*4
2023 results: 57% (2022: 49%)
Japan 62 % (2022: 58%), overseas 52% (2022: 38%)
*By 2030, 100% of the electricity purchased will be sourced from renewable energy
2023 results: Japan 100% (2022: 98 %), overseas 53% (2022: overseas 40%)
-
* 4 Kao is a member of the international initiative RE100, which aims to power businesses using 100% renewable electricity.
-
By 2030, Kao will have reduced CO2 emissions (absolute value) throughout the product lifecycle*5 by 22% (taking 2017 as the base year)*6
2023 results: 15% (2022: 6%)
-
* 5 The volume of CO2 emissions deriving from raw materials procurement, manufacturing, transportation, product usage, and disposal of used products. This covers Scope 1, Scope 2, and part of Scope 3 emissions.
-
* 6 Certified by the global Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) as a 1.5°C target
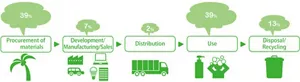
Share of CO2 emissions accounted for by each state of the product lifecycle for Kao products
Looking at different stages of the product lifecycle, procurement of raw materials and product use, which are included in Scope 3, generate a high percentage of CO2 emissions. To reduce emissions, in 2023 Kao continued decreasing its use of raw materials and used recycled plastics when procuring raw materials. In 2023, packaging containers used 6% of recycled plastics. At the product use stage, Kao continues introducing products to reduce water use-related CO2 emissions, for example, concentrated liquid laundry detergent Attack ZERO, which requires only one rinse cycle, and quick-rinsing CuCute dishwashing liquid. The company also asks its major suppliers in the CDP*7 supply chain program to respond to a survey on climate change, forests and water security and provides feedback to support their decarbonization efforts.
-
* 7 A global non-profit that runs the world’s environmental disclosure system for companies, cities, states and regions
At the disposal and recycling stage, Kao is taking new measures to reduce the amount of plastic in packaging containers. In May, the first products making use of film-to-film recycling of used refill packs reached the market. In August, Attack ZERO Perfect Stick, a stick-shaped powdered laundry detergent wrapped in water-soluble film in single-load portions, was launched. Instead of using a hard plastic container, the laundry detergent comes in a pouch, which reduces the amount of plastic used for the product per load*8 . CuCute dishwashing liquid in a bottle-type refill with thinner walls, which reduces plastic use by 40%*9 , was launched in September. In the research and development area, Kao developed a unique production process to create biochemical materials using fermentation production technology, which is known as a production method with low CO2 emissions. Going forward, the company will explore utilizing this technology in its Chemical Business.
-
* 8 In the case of 30-l loads. The Attack ZERO Perfect Stick pouch reduces plastic use by approximately 64% vs. Kao’s non-concentrated liquid detergent bottles
-
* 9 By weight, compared to existing packaging
-
Amount of CO2 emissions reduced as a whole by using Kao’s products and services: 10 million tons by 2030
2023 results: 4,485,000 tons (2022: 4,230,000 tons)
Kao’s Consumer Products Business and its Chemical Business are working to develop products, services and technologies that will contribute to decarbonization in broader society. Kao has set “reduction contribution” as an indicator of the amount of reduced CO2 emissions over product lifecycles between new and existing products and services. The Consumer Products Business has reduced emissions by adopting packaging containers using less plastic and offering water-saving products.
The Chemical Business, working to realize a future Kirei for people, society, and the planet through chemicals, is focusing on enhancing eco-chemical products and coming up with new eco-solutions such as an additive essential for fuel-efficient tires, a cleaning agent that can wash and rinse steel plates at a low temperature, and a toner with low-temperature fixing. Research is also being carried out on developing a saccharification process for converting waste and unused resources into raw material of biochemicals. In 2023, Kao signed an agreement with the Research Association of Biomass Innovation for Next Generation Automobile Fuels*10 to use saccharification enzymes in a research facility for bioethanol production, with the aim of supplying saccharification enzymes for use in manufacturing bioethanol fuel for automobiles.
-
* 10 Members of the Association are ENEOS Corporation, Suzuki Motor Corporation, Subaru Corporation, Daihatsu Motor Co., Ltd., Toyota Motor Corporation, Toyota Tsusho Corporation and Mazda Motor Corporation. With the goal of creating a carbon neutral society, these companies are working together on technological research into the use of biomass and efficient production methods for producing bioethanol fuel for automobiles.
CO2 Related Innovation in Recycling/Targets to Achieve Carbon Negative by 2050 and the 2023 Results
At its Wakayama Research Laboratories, Kao is developing technologies using CO2 as a raw material to implement emissions-reduction measures by 2030.
Since 2021, the Kao Group has been promoting the Kao Group Mid-term Plan with its vision of “protecting future lives” and “sustainability as the only path.” The Kao Group will continue to integrate its ESG strategy into its management practices, develop its business, provide better products and services for consumers and society, and work toward its purpose, “to realize a Kirei world in which all life lives in harmony.”
About the Kirei Lifestyle Plan
Over the past 130 years, Kao has worked to improve people’s lives and help them realize more sustainable lifestyles—a Kirei Lifestyle. The Japanese word ‘kirei’ describes something that is clean, well-ordered and beautiful, all at the same time. The Kao Group established its ESG strategy, the Kirei Lifestyle Plan in April 2019, which is designed to deliver the vision of a gentler and more sustainable way of living. By 2030, Kao aims to empower at least 1 billion people, to enjoy more beautiful lives and have 100% of its products leave a full lifecycle environmental footprint that science says our natural world can safely absorb.
Please visit the Kao sustainability website for more information.
About Kao
Kao creates high-value-added products and services that provide care and enrichment for the life of all people and the planet. Through its portfolio of over 20 leading brands such as Attack, Bioré, Goldwell, Jergens, John Frieda, Kanebo, Laurier, Merries, and Molton Brown, Kao is part of the everyday lives of people in Asia, Oceania, North America, and Europe. Combined with its chemical business, which contributes to a wide range of industries, Kao generates about 1,530 billion yen in annual sales. Kao employs about 34,300 people worldwide and has 137 years of history in innovation.
Please visit the Kao Group website for updated information.
Media inquiries should be directed to:
Public Relations
Kao Corporation
