Simultaneous analysis of ceramides and other intercellular lipids in the stratum corneum
Dermatology
Intercellular lipids in the stratum corneum, which play an important role in maintaining skin moisture and preventing the invasion of external substances, are composed of ceramides, cholesterol, free fatty acids, cholesterol sulfate, and so on. At Kao, we have been developing technologies to understand skin properties by identifying the quantity and quality of intercellular lipids to propose skincare products optimized for each skin concern.
Generally, it is difficult to simultaneously analyze various lipid species with different polarities and chain lengths.
To solve this problem, we use a multi-ionization method that has both properties of electrospray ionization (ESI) and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) in mass spectrometry to detect a wide variety of lipids with high sensitivity.
We devised an ionization promoter to focus on a single ion to be detected in order to avoid the random formation of many ions to be detected from a single lipid molecule.
For absolute quantification, we have synthesized typical ceramides to create calibration curves and corrected the detection sensitivity for ceramides with different chain lengths, enabling quantification of more than 200 molecules of lipids.
Using these analytical techniques*1 , we discovered the ratio of ceramide [NP]/[NS] decreases in response to an increase in trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL), an indicator of skin barrier function*2 .
We will continue to leverage our analytical technologies to propose skincare methods suitable for those with skin troubles.
-
* 1 Kawamoto, A., Yoshida, H., Haneoka, M., Nakamura, S., Kabashima, K., & Takahashi, Y. (2023). Chain Length of Covalently Bound Ceramides Correlates with Skin Barrier Function in Healthy Subjects. Journal of Dermatological Science, 110(1), 35-38.
-
* 2 Yokose, U., Ishikawa, J., Morokuma, Y., Naoe, A., Inoue, Y., Yasuda, Y., Tsujimura, H., Fujimura, T., Murase, T., & Hatamochi, A. (2020). The Ceramide [NP]/[NS] Ratio in the Stratum Corneum is a Potential Marker for Skin Properties and Epidermal Differentiation. BMC Dermatology, 20, 6.
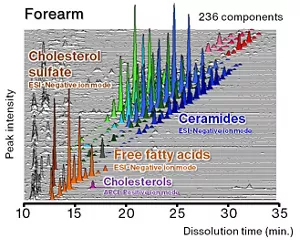
Simultaneous analysis of intercellular lipids
![The correlation between the abundance ratio of ceramide NP to ceramide NS (Cer [NP]/[NS]) and the trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL). The higher the TEWL in the skin is, the lower the Cer [NP]/[NS] becomes. The Cer [NP]/[NS] tends to be lower in the lesional skin of patients with atopic dermatitis than in the skin of healthy subjects.](http://kao-h.assetsadobe3.com/is/image/content/dam/sites/kao/www-kao-com/global/en/innovation/research-development/fundamental/analytical-science/icl-analysis/image-02.jpg?fmt=webp)
Correlation between Cer [NP]/[NS]
and trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL)
Related Information
- Home
- Innovation
- Research & Development
- Fundamental Research
- Analytical Science
- Simultaneous analysis of ceramides and other intercellular lipids in the stratum corneum
- Home
- Innovation
- Research & Development
- Fundamental Research
- Analytical Science
- Simultaneous analysis of ceramides and other intercellular lipids in the stratum corneum
