Computational Chemistry-based Innovative Catalyst Designing
Computational Chemistry
A catalyst is a substance that contributes to the efficient synthesis of target compounds with a low energy and is very important to make economic development consistent with environmental friendliness.
The conventional catalyst development required a long time because an enormous number of candidate catalysts were repeatedly tested for reaction and assessed, depending on experimenter’s knowledge and experience. This was an issue.
Kao tried to reduce the development period by a new, computational chemistry-based catalyst development process. It introduced computation with Neural Network Potential at least 100,000 times faster than the ordinary quantum chemical calculation and virtually conducted catalyst reaction tests in silico, and thereby realized catalyst exploration at least 100 times faster than the conventional process that repeated experiments and assessments (Figure 1).
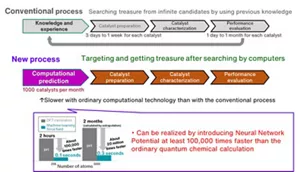
Figure 1
Catalyst screening using Neural Network Potential can computationally predict the performance when a second component is added to the main metal, which allows to determine candidate components to be added (Figure 2).
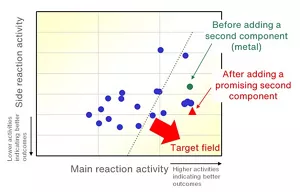
Figure 2
Utilization of computational chemistry-based catalyst-designing technology allows to reduce candidate metals before experiments. The greatly reduced development period with such technology boosts synthesis of environmentally-friendly compounds.
- Home
- Innovation
- Research & Development
- Fundamental Research
- Analytical Science
- Computational Chemistry-based Innovative Catalyst Designing
- Home
- Innovation
- Research & Development
- Fundamental Research
- Analytical Science
- Computational Chemistry-based Innovative Catalyst Designing
