Research on Skin Care Linked to Emotions
Research on Skin Care with a Focus on Stimulation that Creates Pleasant Feelings
Kao Corporation (Kao) has continuously worked on Research on Skin Care Linked to Emotions with a focus on stimulation that creates pleasant feelings since 2012. Kao extracted 12 emotional factors to evaluate emotions while wearing cosmetics and created an emotional assessment scale. With this scale, it was able to objectively understand changes in the state of mind and emotions while wearing cosmetics. Additionally, in 2017, Kao confirmed that the continuous application of a pleasant touch on the facial skin arouses positive emotions and improves skin appearance, demonstrating the effect of a daily skin care ritual.
Kao recently obtained the following research findings through the Research on Skin Care Linked to Emotions.
1) Salivary oxytocin* increases as a result of the application of tactile stimulation that creates pleasant feelings
2) Higher salivary oxytocin level is associated with a higher skin appearance (visual skin condition)
The research results were presented at the 82nd SCCJ Research Debate (Osaka, July 12, 2018).
-
* Oxytocin:
One of the hormones synthesized in the hypothalamus of the brain. Research has revealed that its secretion is promoted by positive physical contact.
Oxytocin has functions to establish emotional attachment in relationships, reduce stress, and stabilize emotions.
Based on past research results, Kao will further build on its study of skin care with a focus on the physiological effects of stimulation through the five senses.
Recent research findings
Kao examined the effect of the physiological changes due to tactile stimulation that creates pleasant feelings on the skin condition under the following testing conditions:
Study 1
Subjects: 33 women aged 20-49 years without major skin problems
Study method: Saliva was collected before applying tactile stimulation and 4 weeks after the application. Changes in salivary hormones, including oxytocin, were evaluated.
Kao instructed the subjects to continuously apply stimulation on the outer forearm using a cheek brush, which reportedly creates pleasant feelings. Stimulation was applied at a speed of about 3 cm/s, with a load of about 20-40 g, twice a day (morning and night, 3 min/time) for 4 weeks (continuous application of tactile stimulation). Saliva was collected before and after the application of tactile stimulation, and changes in salivary hormones were evaluated.
Study results: It was confirmed that salivary oxytocin increases due to the continuous application of tactile stimulation, which creates pleasant feelings (Fig. 1).
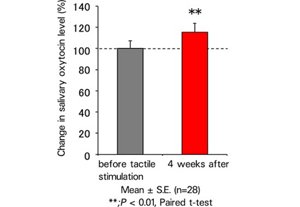
Fig.1: Continuous tactile stimulation and changes in hormone level (oxytocin)
Study 2
Subjects: 89 women aged 20-49 years without major skin problems
Evaluation items:
(1) Salivary oxytocin level was measured.
(2) Participant's skin appearance (visual skin condition) was evaluated using a 7-point response [-3 (most negative) to 3 (most positive)]by sensory experts trained in visual assessment using the evaluation parameters of skin appearance.
Evaluation results:
A weak positive correlation was demonstrated between the salivary oxytocin level and the skin appearance score (skin texture, skin tone evenness, complexion, and skin surface smoothness) (Table1).
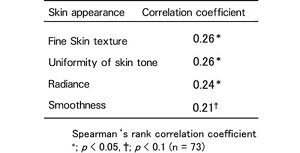
Table 1: Relationship between the oxytocin level and
skin appearance
Study 3—Confirmatory study to verify the results of study 1 and 2
Subjects: 40 women aged 20-49 years without major skin problems
Confirmatory method:
Kao instructed them to include the following behavior in their skin care routine and repeat the entire course five times: to touch softly the facial skin with the palms of both hands for 30s, remove their hands, and rest for 30s. The following evaluations were conducted before and after the application of tactile stimulation:
1) Saliva was collected and the change in the level of oxytocin after the application of tactile stimulation was calculated.
2) The evaluated value of pleasant feelings was represented on a 10-cm visual analog scale to calculate the difference before and after the tactile stimulation (level of pleasant feelings created by the stimulation).
The results showed a weak positive correlation between the change in salivary oxytocin level and the difference in the evaluated value of pleasant feelings before and after applying tactile stimulation to the facial skin (level of pleasant feelings created by the stimulation) (Fig. 2).
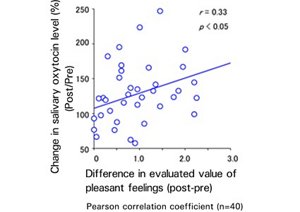
Fig.2: Relationship between the change in the level of oxytocin and level of pleasant feelings created by tactile stimulation
Conclusion:
It was suggested that the oxytocin level within the body increases and skin texture improves as more pleasant feelings are created by tactile stimulation during skin care, such as covering the face with the palms.
Past research findings from the Research on Skin Care Linked to Emotions
1. Extracted 12 factors to evaluate emotions while wearing cosmetics and created an emotional assessment scale
Kansei Science Research of Kao Corporation (Michitaka Sawada, President) conducted three studies on emotional changes*1 to extract 12 emotional factors to evaluate emotions while wearing cosmetics and create an affect scale for cosmetics behavior (Table 2).
Previously, it was impossible to objectively understand changes in the mental state and emotions while wearing cosmetics.
The newly created emotional evaluation scale made it possible to visualize changes in emotion while wearing cosmetics and to measure it objectively. Using the evaluation scale, Kao is currently working to verify the effect of cosmetic feel and hand touching on the users' skin. Subsequently, Kao will examine the relationship between emotional changes and skin condition (skin appearance), and apply the results to research on skin care linked to emotions.
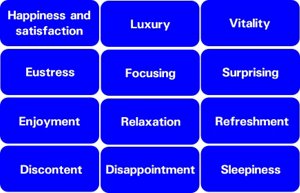
Table 2: an affect scale for cosmetics behavior (12 factors)
feelings created by tactile stimulation
2. Continuous application of a pleasant touch on the facial skin evokes positive emotions and improves skin appearance -The effect of a daily skin care ritual was confirmed-
Kao's Kansei Science Research, Skincare Products Research, Makeup Products Research, Biological Science Research are conducting research on the effect of a daily skin care ritual and recently obtained the following research findings:
1) Tactile stimulation on the facial skin included in the skin care behavior creates pleasant feelings*1
2) Continuous application of a pleasant touch on the facial skin, which arouses positive emotions, improves the visual skin condition (skin appearances) and its effect is associated with the amount of pleasant feelings obtained.*2
-
* 1 The "Effect of daily skin care behavior (tactile stimulation) on the human psychological/physiological index" confirmed in the research has already been published in the Japanese Journal of Physiological Psychology and Psychophysiology (2018) and at the 35th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Physiological Psychology and Psychophysiology (2017.05.27-28)
-
* 2 "A study on the effect of positive emotion on skin appearance" confirmed in the research were announced at the 80th research discussion session of SCCJ (2017.07.13).
SCCJ: The Society of Cosmetic Chemists of Japan
Conclusion:
・It was demonstrated that a wide variety of pleasant feelings can be created by tactile stimulation during skin care, such as covering the face with the palms.
・It was suggested that positive feelings evoked by a hand press ritual contributed to improving skin conditions.
About Kao
Kao creates high-value-added products that enrich the lives of consumers around the world. Through its portfolio of over 20 leading brands such as Attack, Bioré, Goldwell, Jergens, John Frieda, Kanebo, Laurier, Merries and Molton Brown, Kao is part of the everyday lives of people in Asia, Oceania, North America and Europe. Combined with its chemical division, which contributes to a wide range of industries, Kao generates about 1,500 billion yen in annual sales. Kao employs about 33,000 people worldwide and has 130 years of history in innovation. Please visit the Kao Group website for updated information.
Media inquiries should be directed to:
Corporate Communications
Kao Corporation
