Application of an Amphiphilic Polymer Network Gel to a Liquid Foundation
Polymer Chemistry
Foundations are items essential for everyday makeup to conceal color unevenness of the skin and create beautiful skin.
However, the thicker the application of foundation to cover color unevenness of the skin, the further from the texture of bare skin the finish becomes and the less natural it looks. Therefore, it has previously been difficult to cover the skin sufficiently and make a naturally lustrous and non-chalky finish at the same time.
To solve this long-standing problem, Kao has developed a liquid foundation that makes the most of the skin’s natural color and texture, and it beautifully covers the skin at the same time. This is achieved by applying an amphiphilic polymer (polymer containing both water-attracting and water-repelling components) made of unique materials that has an affinity for oil, water, and skin.
The amphiphilic polymer network gel in which a color oil (an oil agent in which a powder pigment is highly dispersed) is wrapped adheres evenly to the skin, creating smooth and wet-looking luster and developing a bright color.
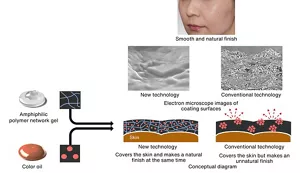
This technology enabled us to develop a foundation that naturally covers the skin without making it look chalky, and brings out the skin’s natural, lively luster—which conventional foundations could not do. This foundation provides a beautiful finish so natural that you may forget you’re wearing it*1 .
We will continue to develop products that make our many customers shine even more beautifully.
-
* 1 Tochioka, S. (2023). Development of a W/O Foundation with Amphiphilic Polymer Networks Achieving Both Coverage and Naturalness. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. Jpn, 57(3), 242-250.
- Home
- Innovation
- Research & Development
- Product Development Research
- Make Up
- Application of an Amphiphilic Polymer Network Gel to a Liquid Foundation
- Home
- Innovation
- Research & Development
- Product Development Research
- Make Up
- Application of an Amphiphilic Polymer Network Gel to a Liquid Foundation
