Precise Interface Control that Supports Food Security
Interfacial Chemistry and Biological Chemistry
As the natural environment and weather have been dramatically changing worldwide, considering sustainable food security has become an urgent task. So Kao is aiming to develop technologies that enable stable and increased production of food.
We are working on the development of adjuvants (assistive agents) that maximize the effect of agricultural chemicals, which are essential for food production, and significantly reduce the usage of such chemicals. For droplets of an agricultural chemical to wet and cover hydrophobic (water-repelling) plant leaf surfaces, it is necessary to reduce the surface tension of the droplets. However, conventional surfactants have not been able to do this well.
To solve this problem, we have been searching for base materials that not only reduce the surface tension of liquid but also effectively work on hydrophobic solid surfaces.
As a result, we have developed a revolutionary technology for significantly reducing surface tension at the interface between liquid and solid. By taking advantage of this technology, we succeeded in putting a functional adjuvant with high wettability into practical use (Figure 1).
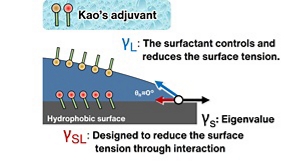
Figure 1 Wettability of the functional adjuvant and mechanism by which it functions
We are also working on the development of adjuvants for drones that help to save labor in next-generation agriculture by newly developing an evaporation suppression technology and a drift (scattering) suppression technology and combining them with this technology (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Application of the characteristics of the functional adjuvant to a technology for suppressing the drift (scattering) of droplets sprayed by a drone
In the future, we will contribute to food security and support a sustainable future for food by developing products that take advantage of our interface control technologies from the perspectives of various fields, including soil conditioners and feed for oceanic farming.
Kao Wettability evaluation of Kao adjuvant
The following video does not include audio, and a text transcription of its visual content is available.
A transcript is available here.
This video compares the wettability of liquids dropped onto plant leaves (standard speed).
The series of images on the left shows the wettability of water alone, indicating that the wetting does not spread. The series in the right shows the wettability of water with Kao’s functional spreading agent added, indicating that the wetting spreads rapidly.
Kao Effect of Kao adjuvant for drone to control dispersal
The following video does not include audio, and a text transcription of its visual content is available.
A transcript is available here.
This video shows how liquids drift when sprayed from a height of 2 m with the crosswind blowing at 3 m per second.
The series of images on the left shows how water alone drifts, indicating that it easily scatters (drifts) in the wind. The series on the right shows how water with Kao’s functional spreading agent added drifts, indicating that it is not easily scattered by the wind (drift is suppressed).
- Home
- Innovation
- Research & Development
- Fundamental Research
- Material Science
- Precise Interface Control that Supports Food Security
- Home
- Innovation
- Research & Development
- Fundamental Research
- Material Science
- Precise Interface Control that Supports Food Security
